Extracting data from multiple rasters using point profiles with Arcview GIS/ArcGIS
How to work with the data extraction extension for Arcview and equivalent operation for ArcGIS
Обсудить в форуме Комментариев — 0
Necessary step in creating spectral profiles, assessing raster datasets accuracy and others tasks of this kind is extraction of values from multiple rasters using certain point objects. Unlike zonal statistics, where object is the polygonal object and several parameters can be calculated, data extraction for point data is only getting actual values.
As a profile any set of any number of points can be used in the form of shape-file.
Values are extracted from raster files in GRID format or single and multi-band image, added as themes to the View table of contects (TOC). In case of images, they should be loaded as Image themes, to work with ERDAS IMAGINE IMG files IMAGINE Image Support extension should be switched on first to be able to load them. For this extension to function, Spatial Analyst should be present and loaded. Number of GRIDs/images is not limited, but loading hundreds of them in TOC can make Arcview freeze temporarily. If more than 50 rasters are needed to be loaded in TOC - split them in portions by 50 files and load them portion by portion.
Input rasters can be either integer or floating, for each raster its type will be determined and the field in the shape-file will be assigned the same type. Signed 16-bit images with negative values can be imported incorrectly (not tested yet).
In process of calculation, value will be derived for each point in the shapefile, for each raster theme in TOC. During calculation, NODATA pixels are ignored and no data is extracted from such points.
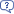
For each raster theme in the attributive table of the point shape-file new field will be created automatically, the name of the field will be equal to the name of the raster theme. If you have 6 points and 100 raster themes in the view, there will be 600 extractions carried out by the extension and 100 new fields created and populated with the values of the selected parameter. The ability to get values for multiple rasters is the unique feature of this extension. This ability is especially useful for extracting data from any kind of time-series (for example - NDVI (rus)).
Data extraction is processor intensive, for example: extracting information using 200 points from 10 rasters using Pentium IV, 1Gb memory PC will take approximately 15 minutes.
Extension can work both with projected and unprojected view.
To start using it in Arcview GIS, you need:
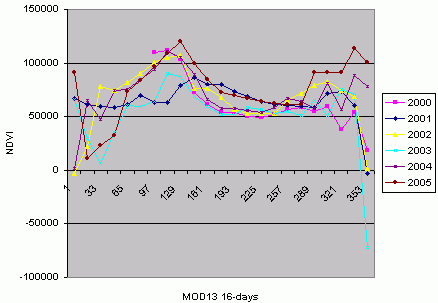
- Turn on Spatial Analyst (File\Extensions\Spatial Analyst)
- Download and turn on extension extractdata.avx (File\Extensions\Extract data...)
- Load points theme and raster themes from which you want to extract data in table of contents of the view.
- Select point theme and press
 .
. - It is also possible to perform calculations for a subset of a theme, to do this select records/objects which you'd like to use (they'll be marked in yellow) and press
 .
.
Equivalent operation can be performed in ArcGIS using one of the tools from Arctoolbox: Spatial Analyst Tools\Extraction\Extract values to points. As the result of this operation, new point shape-file will be created, which will include all the fields with values from the initial shape-file, plus new field with extracted values. Spatial Analyst should be installed, licensed and turned on: Tools\Extensions\Spatial Analyst. This instrument takes in only one raster at a time. To sample multiple raster Sample instrument from the same group is needed, it can work with multiple rasters and generates a table.
If source data is in image format (but not GRID) and it is multiband, you might want to look at different strategy to extract information for each pixel within the zone defined by polygons or as mean/sum etc for the zone defined by polygon.
Обсудить в форуме Комментариев — 0
Ссылки по теме
Последнее обновление: September 09 2021
Дата создания: 30.12.2006
Автор(ы): Максим Дубинин
© GIS-Lab и авторы, 2002-2021. При использовании материалов сайта, ссылка на GIS-Lab и авторов обязательна. Содержание материалов - ответственность авторов. (подробнее).